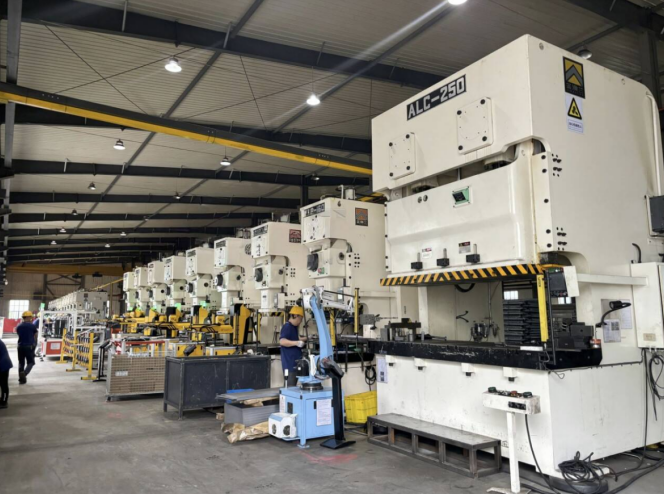
Mechanical press
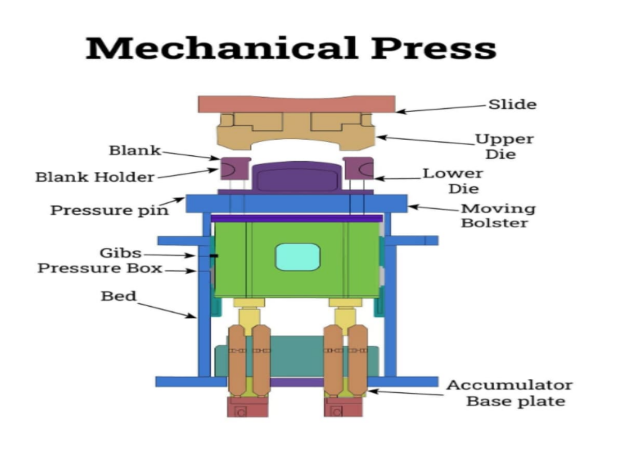
Working principle: It mainly uses a motor connected to a mechanical flywheel to transmit and store energy. The motor drives the flywheel to rotate, and drives the gears, crankshafts, connecting rods and other moving parts through the clutch, converting the circular motion into the linear reciprocating motion of the slider, thereby driving the punch to apply pressure to the metal material.
Features
Application scenarios: More suitable for manufacturing shallower and simpler parts from metal sheet coils, usually used for progressive and transfer stamping in large-scale production, such as automotive parts, electronic components, hardware products and other industries1.

Technical specifications
Specification | Value |
Pressure Force | 200 tons |
Motor Power | 15 kW |
Throat Depth | 400 mm |
Strokes per Minute | 40 spm |
Stroke Adjustment | 20 - 170 mm |
Max. Closed Mould Height | 430 mm |
Distance Between Table and Ram | 600 mm |
Ram Adjustment | 80 mm |
Table Size | 800 ×1200 mm |
Ram Size | 400 ×700 mm |
Table Height | 950 mm |
Ø Hole in the Table | 300 mm |
Ø Hole in the Ram | 60 mm |
Total Width (Frontal) | 2130 mm |
Total Length | 2100 mm |
Overall Height | 3250 mm |
Features | Central motorized lubrication, hydraulic overload protection, electro-pneumatic clutch and brake, safety light guards, PLC control, adjustable stroke, anti-vibration pads |
Optional Accessories | Inverter, pneumatic/hydraulic die ejector, lower auxiliary table, strain gauge system, NC digital display |
Drive system of power press
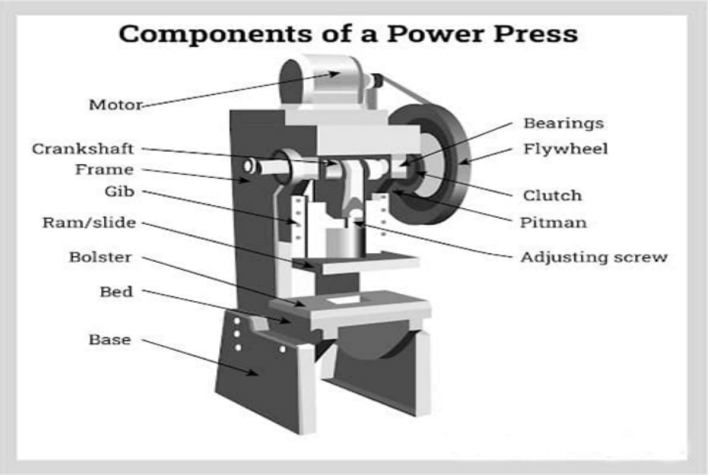
The drive system of a power press is a key component that provides power for the machine to operate. In a hydraulic press, the plunger movement is driven by a hydraulic cylinder and piston rod, which are usually located on both sides of the press.
Hydraulic systems are able to withstand large loads and longer strokes continuously. On the other hand, mechanical drive systems consist of components such as cranks, flywheels, eccentrics, and toggles. The flywheel rotates, connecting the crank to drive the movement of the slide, providing a strong mechanical drive force that is very suitable for blanking and stamping processes.
Pneumatic presses use compressed air to operate and have a relatively simple structure. The power comes from the movement of compressed air, which makes it very fast and can quickly drive the plunger. In short, each type of drive system has its own advantages and is suitable for different metalworking processes.
Hydraulic Press
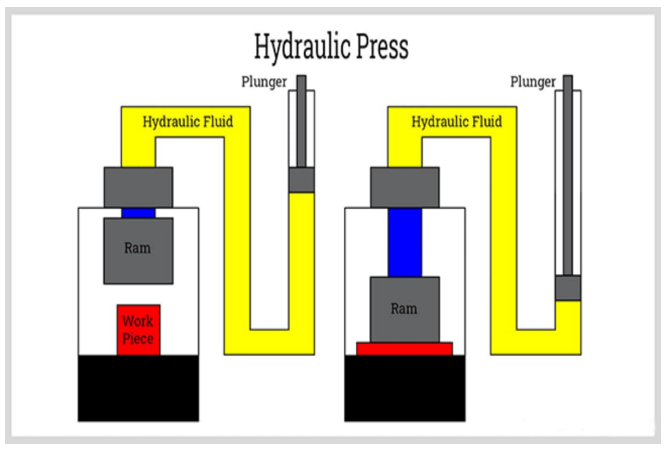
Working Principle: Based on Pascal’s Law, pressurized hydraulic fluid is used to apply force to the material, displacing the fluid with a force level proportional to the hydraulic piston displacement and the piston head diameter, providing advanced control over the amount of pressure2.
Features
High pressure: A high pressure can be generated, and the size of the press usually ranges from 20 tons to 10,000 tons, which can meet the processing needs of large parts1.
Application scenarios: Typically used for smaller production runs to create more complex and deeper stampings than mechanical presses, widely used in metal forming, forging, stamping, mold making, deep drawing, die casting and other fields, also used in automotive manufacturing, aerospace, home appliances and other industries.
Technical specifications
Specification | Value |
Capacity | 600 tons |
Height | 5300 mm (+/-100 mm) |
Width | 1500 mm (+/- 100 mm) |
Table Area (Width) | 3000-5000 mm |
Table Area (Height/Length) | 1200 - 1500 mm |
Minimum Work Capacity | 1150 mm |
Distance Between Trays (Max) | 2300 mm |
Piston Stroke (Min) | 500 mm |
Pump | 500-90 1/min |
Tank Capacity (Min) | 670 L |
Type | C-Type |
Travel Speed (Max) | Approach: 18 mm/sec
Working: 5 mm/sec
Backward:20 mm/sec |
Integrated Crane Capacity | Min 3 Ton at 2 meters |
Travel Speed (Crane) | Free: 80 mm/s
Under Load: 5 mm/s |
Controls | Manual with remote control |
Stroke/Pressure | Adjustable |
Instrumentation | Analogue & digital |
Electrical Supply | 3¢, 415 V, 50Hz |
Safety Features | Mesh Guarding, Interlocked light guards, Safety valve, Auto stop |
Warranty | Min 12 months |
Installation and Commissioning | By the firm |
Mechanical servo press
Working Principle: Using a high capacity motor instead of a flywheel, powered by a connecting rod assisted drive system or a direct drive system, the movement of the slide is precisely controlled by a servo motor to achieve precise control of the stamping process.
Features
High Precision: Stroke, slide position and movement, and speed are all controlled and programmable, enabling high-precision stamping processes and the manufacture of more complex stampings.
Application scenarios: Mainly used in situations where high stamping accuracy and efficiency are required, such as precision electronic components, automotive parts, aerospace parts, etc..

In Conclusion
Today, many mechanical and hydraulic presses are enhanced with computer numerical control (CNC) systems. Presses are essential in the sheet metal industry because they can perform a variety of metalworking tasks such as cutting, bending, punching, and forming.
The most effective machines for bending workpieces are press brakes and panel bending machines. These industrial processing machines have been around for decades and are still popular. With 20 years of expertise in sheet metal machinery production, LANGYE offers a wide range of products including press brakes, panel bending machines, laser cutting machines and shearing machines.
Our sales team can help you select the machine that meets your needs while ensuring the most cost-effective solution. Browse our products or contact our sales team to learn more about our products and their pricing.
 English
English